New drone rules Canada are changing the game for both recreational and commercial drone pilots. These updated regulations aim to improve safety and manage the increasingly popular use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) across the country. Understanding these new rules is crucial, whether you’re a seasoned drone enthusiast or just starting out, to ensure you’re flying legally and responsibly.
This guide breaks down the key aspects of the new regulations, covering everything from registration and licensing to operational restrictions and safety guidelines. We’ll also explore the impact on various industries and discuss the future of drone regulation in Canada. Get ready to take flight—safely and legally!
Overview of New Drone Regulations in Canada
Canada’s drone regulations have undergone significant updates to ensure safe and responsible operation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). These changes impact various aspects of drone ownership and operation, from registration and licensing to operational restrictions and safety protocols. The updated regulations aim to balance the burgeoning use of drones across various sectors with the need to mitigate potential risks to public safety and privacy.
Key Changes in Updated Drone Regulations
Key changes include stricter registration requirements, clearer operational restrictions, enhanced licensing categories for commercial operators, and increased penalties for violations. The classification system for drones has also been refined, aligning with international standards. The rationale behind these changes is to improve safety, enhance accountability, and streamline the regulatory framework for the growing drone industry.
Drone Categories Affected by Regulatory Changes
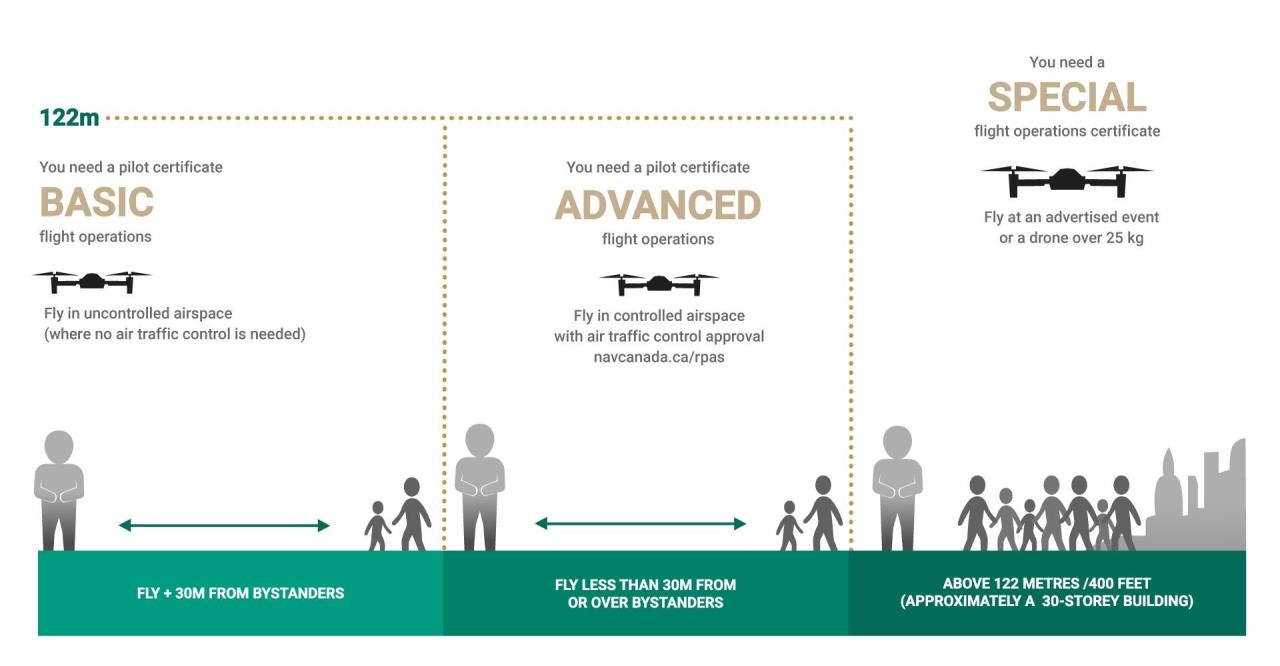
The changes affect all categories of drones, from small recreational models to large, complex commercial UAVs. However, the specific requirements vary depending on the drone’s weight, intended use, and operational complexity. For instance, heavier drones and those used for commercial purposes face more stringent registration and licensing requirements than smaller, recreational drones.
Rationale Behind Regulatory Changes
The driving force behind these regulatory changes is a multifaceted approach to safety and responsible drone operation. The increase in drone usage necessitates a clear and comprehensive regulatory framework to prevent accidents, protect privacy, and ensure compliance. The changes aim to strike a balance between fostering innovation in the drone industry and mitigating potential risks.
Registration and Licensing Requirements
Registering and licensing your drone in Canada is crucial for legal and safe operation. The process varies based on the drone’s classification and intended use. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties.
Step-by-Step Guide to Drone Registration
- Determine your drone’s weight and intended use (recreational or commercial).
- Visit the Transport Canada website and access the online registration portal.
- Provide necessary information about yourself and your drone (model, serial number, etc.).
- Pay the registration fee.
- Receive your registration confirmation and affix the registration number to your drone.
Drone License Types and Prerequisites
Different types of drone licenses cater to various levels of operational complexity and risk. Recreational drone operation generally doesn’t require a specific license beyond registration, while commercial use mandates specific certifications and training. These licenses ensure operators possess the necessary skills and knowledge for safe and responsible operation.
Comparison of Registration Processes for Different Drone Classes
The registration process for different drone classes primarily differs in the level of detail required and the associated fees. Larger, heavier, and commercially operated drones require more extensive documentation and a more rigorous review process compared to smaller, recreational drones. The complexity of the registration process scales with the potential risk associated with the drone’s operation.
Operational Restrictions and Safety Guidelines
Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount. Several geographical areas restrict or prohibit drone flights, and specific safety protocols must be followed to avoid accidents and legal repercussions. Penalties for violations are substantial.
Restricted and Prohibited Geographical Areas
Drone operation is restricted or prohibited near airports, sensitive infrastructure (power plants, military bases), and populated areas without proper authorization. No-fly zones are frequently updated, so operators must consult official sources before each flight. Operating a drone in a restricted area can lead to significant fines and legal action.
Drone Operator Safety Protocols
Operators must maintain visual line of sight with their drone at all times, unless operating under specific exemptions. They must also respect privacy laws, avoid flying over people, and operate their drone responsibly and safely, adhering to all relevant regulations. Regular maintenance and pre-flight checks are crucial.
Penalties for Violating Drone Regulations
| Offense | Penalty | Applicable Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Operating a drone without registration | Up to $3,000 CAD | Canadian Aviation Regulations (CARs) |
| Flying a drone in a restricted airspace | Up to $100,000 CAD and/or imprisonment | CARs |
| Causing damage or injury through negligent drone operation | Variable, depending on severity; could involve significant fines and legal action | CARs and other relevant legislation |
Drone Insurance and Liability: New Drone Rules Canada
Securing appropriate drone insurance is crucial for Canadian operators to protect themselves against potential liability. The type and extent of coverage depend on the drone’s use and potential risks.
Importance of Drone Insurance, New drone rules canada
Drone insurance provides financial protection against accidents, property damage, and third-party liability claims. It safeguards the operator from potentially devastating financial consequences arising from incidents involving their drone. The cost of repairing or replacing a damaged drone, let alone compensating for injuries or property damage caused by it, can be substantial.
Types of Drone Insurance Coverage
Common coverage options include liability insurance (protecting against claims from third parties), hull insurance (covering damage to the drone itself), and potentially additional coverage for loss of business income or legal defense costs. The specific coverage options and their cost will vary depending on the insurer and the nature of the drone operation.
Scenarios Where Drone Insurance is Crucial
Examples where drone insurance is vital include a drone crashing into a building, causing damage; a drone colliding with another aircraft; or a drone capturing images that infringe on someone’s privacy, leading to a lawsuit. In all these cases, adequate insurance would mitigate the financial burden on the operator.
Technological Advancements and Regulatory Adaptation

Rapid advancements in drone technology, such as autonomous flight and beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) operations, present both opportunities and challenges for regulators. Adapting regulations to keep pace with these advancements is crucial to ensure safe and responsible innovation.
Impact of Technological Advancements on Regulations
Autonomous flight capabilities and BVLOS operations require new regulatory frameworks addressing safety concerns related to increased complexity and potential for accidents. Regulations need to evolve to accommodate these technologies while ensuring public safety and preventing misuse.
Challenges of Adapting Regulations to Technological Advancements
The rapid pace of technological innovation often outstrips the ability of regulatory bodies to keep up. Developing effective regulations for emerging technologies requires careful consideration of safety, security, and privacy concerns, while also fostering innovation. Balancing these competing interests is a significant challenge.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating Regulatory Challenges
Imagine a future scenario with swarms of autonomous delivery drones operating in urban environments. Regulating the airspace, ensuring collision avoidance, managing data security, and addressing potential disruptions to air traffic would pose immense regulatory challenges, requiring innovative solutions and international collaboration.
Impact on Various Industries
The new drone regulations significantly impact various industries that utilize drones for commercial purposes, requiring adaptation and compliance with the updated rules. The regulatory landscape differs between commercial and recreational use.
Impact on Agriculture, Construction, and Filmmaking

Industries like agriculture (precision farming), construction (site surveying), and filmmaking (aerial cinematography) rely heavily on drones. The new regulations necessitate updated operational procedures, specialized training for operators, and investment in compliant technologies to ensure continued operation within the legal framework.
Comparison of Commercial and Recreational Drone Use
Commercial drone use faces stricter regulations, including licensing requirements, operational limitations, and higher insurance standards compared to recreational use. The higher level of risk associated with commercial operations necessitates a more rigorous regulatory framework.
Industry Adaptation Examples
- Agriculture: Farms are integrating drone flight planning software that adheres to no-fly zones and ensures compliance.
- Construction: Companies are investing in training programs for their drone pilots to meet the new licensing requirements.
- Filmmaking: Production companies are working with specialized drone service providers who hold the necessary licenses and insurance.
Public Awareness and Education
Transport Canada plays a key role in educating the public about safe drone operation and regulations. Increased public awareness is crucial for minimizing accidents and promoting responsible drone use.
Transport Canada’s Role in Public Education
Transport Canada provides resources, educational materials, and online information to educate the public about drone regulations, safety protocols, and best practices. They also conduct outreach programs and work with industry stakeholders to promote safe drone operation.
Methods for Improving Public Awareness
Improved public awareness can be achieved through targeted public awareness campaigns, educational workshops, collaboration with community organizations, and the use of social media and online platforms to disseminate information. Clear and accessible information is key.
Sample Public Service Announcement (PSA)
“Before you fly your drone, know the rules! Check for no-fly zones, keep your drone in sight, and respect people’s privacy. Flying safely is everyone’s responsibility.”
So, Canada’s got some new drone rules, right? It’s all about safety and responsible flying. Thinking about amazing drone displays though, check out the planned spectacle at the china new year drone show 2042 – it’s a whole different level! Then, back to Canada – remember to register your drone and follow those new rules to avoid any trouble.
Comparison with International Drone Regulations
Canadian drone regulations share similarities with other countries but also exhibit unique aspects. Understanding these differences is crucial for international drone operations.
Comparison with USA, UK, and Australia
The USA, UK, and Australia have similar regulatory frameworks focusing on registration, licensing (for commercial use), and operational restrictions. However, specific requirements, such as weight classifications and licensing processes, may differ. For example, the specific no-fly zones and licensing requirements might vary based on national security priorities and airspace management practices.
Areas of Stringency in Canadian Regulations
Canadian regulations may be stricter in certain areas compared to other countries, reflecting national priorities and safety standards. For example, penalties for violations might be higher in Canada compared to some other jurisdictions.
Implications for International Drone Operations
International drone operations require careful consideration of the regulations of each country involved. Operators must ensure compliance with the local regulations of their destination country to avoid legal penalties and operational issues. Understanding these differences is crucial for smooth and legal cross-border drone operations.
Future Trends and Predictions for Drone Regulation
Future drone regulations in Canada will likely adapt to technological advancements and evolving safety concerns. Predicting these changes requires considering emerging technologies and their potential impact.
Potential Future Changes to Canadian Drone Regulations
We can expect further refinements in licensing categories, potentially incorporating advanced certifications for autonomous flight and BVLOS operations. Regulations will also likely address issues related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and the integration of drones into increasingly complex airspace environments. More stringent enforcement mechanisms and penalties are also likely.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Future Regulations
Emerging technologies like AI-powered autonomous drones, drone swarms, and advanced sensor systems will necessitate new regulatory frameworks addressing issues of safety, liability, and data security. These frameworks must balance fostering innovation with mitigating potential risks.
Long-Term Implications of Regulatory Trends

The long-term implications of these regulatory trends will be a more sophisticated and nuanced regulatory framework, better equipped to handle the complexities of advanced drone technologies. This will likely lead to increased safety, reduced risk, and a more robust and sustainable drone industry in Canada. However, the balance between innovation and regulation will remain a crucial consideration.
Last Recap
Navigating the new drone rules in Canada might seem daunting at first, but with a clear understanding of the regulations and a commitment to safe flying practices, you can confidently enjoy the benefits of drone technology. Remember to always check for updates and stay informed about evolving regulations. Safe and responsible drone operation benefits everyone – protecting both people and property, while fostering the continued growth and acceptance of this innovative technology.
Happy flying!
Query Resolution
What happens if I don’t register my drone?
Failure to register your drone can result in fines.
Can I fly my drone at night?
Night flights are generally restricted unless you have specific authorization.
What kind of insurance do I need for my drone?
So, you’re brushing up on the new drone rules in Canada? It’s good to be informed before you fly! Thinking about impressive drone displays? Check out the amazing spectacle of the shanghai dragon drone show to see what’s possible. Understanding the Canadian regulations is key, though, to ensuring your own drone flights are safe and legal.
The type of insurance depends on your drone’s use (recreational or commercial) and the level of risk involved. Liability insurance is often recommended.
Where can I find a list of no-fly zones in Canada?
So, you’re brushing up on the new drone rules in Canada? That’s smart, because knowing the regulations is key. To help visualize some of the complexities, think of it like navigating the challenges in the vip 3 squid game ; lots of potential pitfalls! Getting your drone license and understanding airspace restrictions is just as crucial as knowing the rules of the game itself if you want to avoid trouble with the new Canadian drone laws.
Transport Canada’s website provides a map and resources detailing restricted airspace.
How do I appeal a penalty for violating drone regulations?
The process for appealing penalties is Artikeld in Transport Canada’s documentation. You’ll typically need to submit a formal appeal within a specific timeframe.
